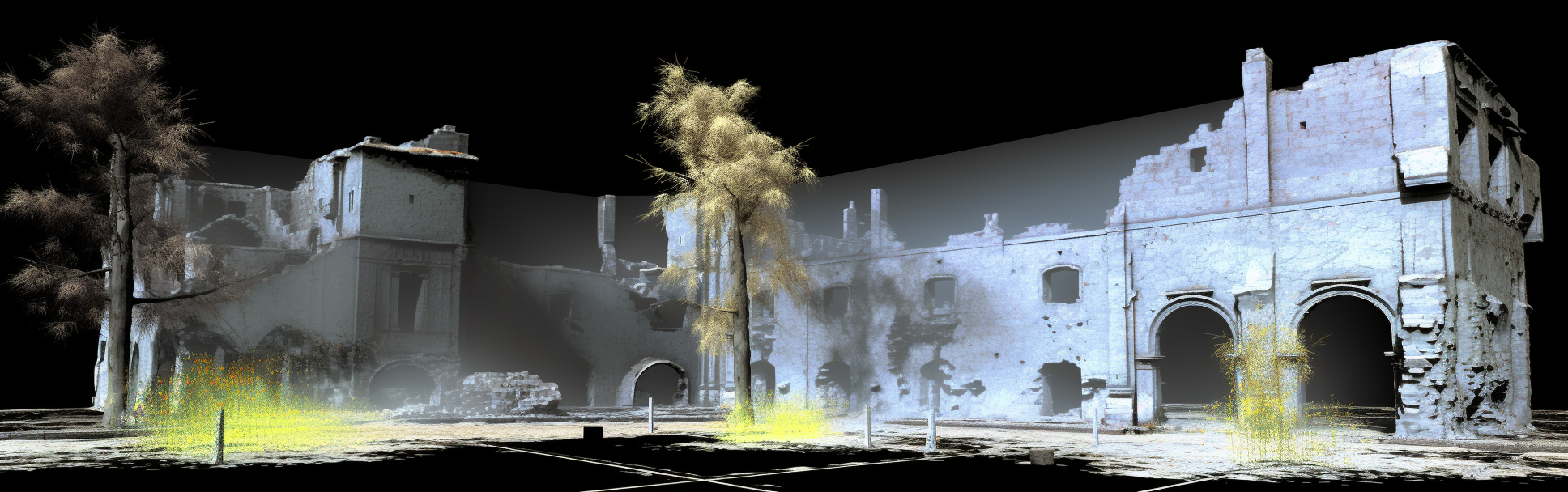
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is one of the oldest and most reliable techniques for 3D reconstruction. It involves capturing a series of photographs from different angles and using them to create a 3D model of an object or environment. The beauty of photogrammetry lies in its simplicity and accessibility; all you need is a camera and some specialized software.Pros and Cons
- Pros: Highly accurate, accessible, and cost-effective. It’s a technology that has been refined over decades, making it a go-to choice for many professionals in fields ranging from archaeology to filmmaking.
- Cons: However, photogrammetry is not without its limitations. It requires a controlled environment and can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with complex structures.
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF)
Neural Radiance Fields, or NeRF, is a more recent entrant in the field of 3D reconstruction. Unlike Photogrammetry, which relies on traditional imaging techniques, NeRF employs machine learning algorithms to create a 3D model from a set of 2D images. The technology is particularly exciting because it allows for the generation of highly detailed and realistic models without requiring specialized hardware.Pros and Cons- Pros: NeRF’s strength lies in its ability to handle complex geometries and lighting conditions, offering a level of detail that is often hard to achieve with other methods.
- Cons: On the flip side, the technology is computationally intensive, often requiring powerful hardware and longer processing times.
Gaussian Splatting
Gaussian Splatting is perhaps the least known among the three technologies but is no less fascinating. It’s a rendering technique that uses Gaussian functions to blend and smooth out the visual elements in a 3D model. This method is particularly useful for creating more natural and fluid transitions between different parts of a model, making it ideal for applications that require high levels of realism.Pros and Cons- Pros: One of the standout features of Gaussian Splatting is its ability to produce incredibly smooth and realistic textures. This makes it highly suitable for applications where visual fidelity is paramount.
- Cons: However, like NeRF, Gaussian Splatting is computationally demanding and may require specialized hardware for optimal performance.
Comparison
While Photogrammetry, NeRF, and Gaussian Splatting each offer unique approaches to 3D reconstruction and rendering, they also share common goals: to capture the essence of the real world in a digital format. Photogrammetry excels in its accessibility and proven track record, making it a reliable choice for many professionals. NeRF, with its machine learning capabilities, offers unparalleled detail and complexity but at the cost of computational resources. Gaussian Splatting, although less known, shines in its ability to produce visually stunning and realistic textures.Each technology has its place, depending on the project’s requirements and constraints. Whether you’re an archaeologist looking to digitally preserve an ancient site or a filmmaker seeking to create a lifelike digital environment, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these technologies can guide you in making an informed decision.Benefits of Using a 360 VR Camera
In a world where capturing moments has become almost second nature, 360 VR cameras offer a revolutionary way to experience those moments. Unlike traditional cameras that offer a limited field of view, 360 VR cameras capture the entire surrounding environment. This immersive experience is not just a technological marvel but a new medium of storytelling.Why Hiring a Professional Matters
While 360 VR cameras are becoming more accessible, the expertise required to create truly immersive experiences is something that cannot be easily replicated. Professionals in this field not only have the technical know-how but also the artistic vision to bring these digital worlds to life. Whether it’s setting the right lighting conditions or stitching together images for a seamless experience, the value of professional expertise cannot be overstated.Special Focus: Historical Preservation
By creating detailed 3D models, historical preservationists can monitor the condition of these sites over time, identifying any changes or damages that may occur. This proactive approach not only aids in the maintenance of these sites but also provides an invaluable resource for educational and research purposes. Technologies like Photogrammetry, NeRF, and Gaussian Splatting offer more than just stunning visuals; they serve as vital tools in the preservation and understanding of our shared history.Frequently Asked Questions
What is Photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry is a technique for creating 3D models from 2D photographs. It involves capturing multiple images from different angles and using specialized software to stitch them together into a 3D representation.
How does NeRF work?
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) employs machine learning algorithms to create 3D models from a set of 2D images. It's particularly effective in handling complex geometries and lighting conditions.
What is Gaussian Splatting?
Gaussian Splatting is a rendering technique that uses Gaussian functions to blend and smooth out visual elements in a 3D model, creating more natural and fluid transitions between different parts of a model.
How do 360 VR Cameras differ from traditional cameras?
Unlike traditional cameras that capture a limited field of view, 360 VR cameras capture the entire surrounding environment, providing an immersive experience.
Why should I hire a professional for 360 VR photography?
Professionals have the technical expertise and artistic vision required to create truly immersive experiences. They can handle aspects like lighting, stitching, and post-processing to deliver high-quality results.
Can Photogrammetry be used for historical preservation?
Yes, Photogrammetry is often used to create detailed 3D models of historical sites, providing a valuable baseline for future conservation efforts.
What are the computational requirements for NeRF?
NeRF is computationally intensive and often requires powerful hardware and longer processing times compared to other methods like Photogrammetry.
Is Gaussian Splatting suitable for all types of 3D modeling?
While Gaussian Splatting excels in creating realistic textures, it may not be the best choice for all types of 3D modeling due to its computational demands.
What are the applications of these technologies?
These technologies have a wide range of applications, from entertainment and virtual tourism to medical imaging and historical preservation.
Are these technologies accessible to beginners?
While Photogrammetry is relatively accessible, NeRF and Gaussian Splatting may require a deeper understanding of machine learning and computational graphics, respectively.
Conclusion
In the quest to understand and recreate our world, technologies like Photogrammetry, NeRF, and Gaussian Splatting offer unique and powerful tools for 3D reconstruction and rendering. While each has its strengths and limitations, their collective impact on fields ranging from entertainment to historical preservation is undeniable. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, understanding these technologies becomes not just a professional requirement but a gateway to new forms of storytelling and preservation. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious enthusiast, the future of 3D imaging is a journey worth embarking upon.
